2023 FutureView Design Trend Report
Conscious Calibration
2023 FutureView trend report
Conscious Calibration
Sparked by pivotal changes in humanity, technology, and culture, we believe that this decade marks the Conscious Era of digital transformation. An evolving level of consciousness between humans and machines is driving the need for digital experiences that are more intelligent, immersive, systemic, and social. These four areas of transformation are the guiding forces for conscious experience design and thoughtful product innovation, and they set the framework for our view of the future in 2023 and beyond.
Last year, exuberance drove a hype cycle that touted new technology often at the expense of confirming its alignment with genuine human needs. But today’s climate is adding a dose of reality. A new lens on innovation reveals the need for more practical, useful, and empathetic product design. Product teams are reframing products from aspirational ideals to meaningful realities. Successful products will be borne out of true human insight and real value for people.
Calibrating From Hype to Reality
Over the past year, accelerated technological progress and elevated consumer demand delivered record results for businesses and consumers alike. We witnessed a watershed moment of abundance and growth driven by rapid digital innovation. But as with any acceleration event, we’re now seeing a natural stage of calibration that’s reshaping innovation.
As we start 2023, it’s critical that companies consciously calibrate strategies in the face of economic headwinds. Similar to how an aircraft accelerates after take off and then calibrates its systems to reach an optimal cruising altitude and speed for a more sustainable long-term trajectory, the business innovation continuum requires calibration for long-term performance. Realignment of innovation strategies to navigate more conservative market conditions will prioritize value that’s in tune with user needs and mindsets, and fit naturally into users’ lives. This pragmatic lens focuses innovation on shorter-term realities rather than lofty aspirations that are further out.
The four conscious design themes for 2023

Download FutureView 2023 trend report to learn more about how to drive successful product innovation.
Social
Design for
Essentialism
First Things First
After years of maximalist consumption behaviors, consumers are thoughtfully reevaluating priorities, resources, money, and effort to prioritize products and experiences that provide essential value.
Consumers are narrowing spending and interest as a result. The end of the pandemic in many parts of the world has coincided with an increase of economic, geopolitical, and environmental challenges. The result can be measured in scarcity, more expensive essential goods, and increased human migration. For those consumers who have been lucky enough to avoid calamity, there is an increased focus on the essentials—and an awareness of the fragility of security.
Consumers are prioritizing improving and maintaining physical and mental health—including reevaluating their work. A growing desire for green tech and inclusive solutions indicates that this renewed consciousness is influencing purchasing priorities. At the same time, it’s evident that people are willing to cautiously invest in experiences and activities that align with their current values and mindset. As consumer preferences move from maximalism to essentialism, successful product designers will calibrate their product strategies to align more closely with their users’ priorities.
What We See

People are reexamining daily activities and making changes to build meaning and avoid toxicity across work and life. A 2022 Harvard Business Review article stated that “The Great Resignation” of 2021-22 was actually a “Great Exploration” as many Americans were able to decouple work from geography and were inspired to focus on attaining the most essential, sustainable, and meaningful experiences in their lives.
While in 2023 there is an increase of workers returning to the office, many workers are still spending some portion of each week working remotely, and work location flexibility is becoming the norm. Workers are using this flexibility to support their priorities of increased work-life balance, family connection and an investment in experiences missed during the pandemic. These attitudes are driving several consumer behaviors: an increased reliance on distributed services and technologies that empower work from anywhere; increased demand for and shifting use patterns of transportation infrastructure; and consumers’ willingness to spend on once-in-a-lifetime experiences despite the high costs of many essentials.
“Essentialism is a systematic discipline for discerning what is absolutely essential, then eliminating everything that is not, so we can make the highest possible contribution towards the things that really matter.”
Essentialism: The Disciplined Pursuit of Less | Greg McKeown

Conscious consumerism is driving more ethical purchases and business decisions that ensure products have a positive impact on humanity and the world. Companies that prioritize environmental and societal issues tend to win customers and improve performance. Research shows that 43% of global consumers want to buy more from organizations that benefit society, even if their products or services cost more. And 64% are prepared to behave differently if it benefits society.
Sustainability goals are more prevalent as climate change and pandemic-induced shortages have made people more cognizant of their consumption and their desire for preservation. Research shows that 50% of Gen Z buyers have cut down how much they buy and 45% refrained from purchasing select brands and products based on the company’s perceived “good citizen” and environmental values. Successful brands and products will make sustainability a key dimension of product marketing and distribution.

Consumers are evaluating how their purchases can empower both their lives and their communities. In Europe and North America there is an increased awareness of energy scarcity as war and climate change destabilize existing energy infrastructures. Increases in crime and desperation have made communities eager for new, interconnected solutions. In this environment, products that improve both personal and community resilience will have an edge.
The economic climate and consumer sentiment demand that designers and product strategists focus innovation on products and capabilities that align with individual and community well-being and give users more flexibility, control, and confidence. Examples of successful, empowering products include electric vehicles, valuable for reducing emissions, but also able to serve as a backup source of power in cases of blackouts. Electronics with off-peak charging features that acknowledge the need to customize charging to reduce stress on the grid and on customers’ budgets. And the Ring smart doorbell Neighbors App that can share data with the neighborhood. We believe that well-researched product design strategies, that are calibrated to users’ essential needs in the short term, will provide a pathway to more valuable innovation as future conditions change.
How to Prepare
- Ensure that your product aligns with customers’ essential priorities by measuring innovation against users’ needs of health, safety, connection, and global awareness.
- Build flexibility and user control into experiences and products to deliver the highest level of value. Consider how digital experiences can shift to provide the most essential use cases based on the device surface.
- Consider whether your products can serve both the individual customer and their community. Support consumers in their connection to their communities.
Intelligent
Design for
Cooperation
The Dream Team
In the year ahead, we will witness “cooperative intelligence” lead as an essential core to digital products and services. AI is the defining “conscious” technology of the decade—growing more aware and smarter every day.
But science fiction has led our imaginations to think of artificial intelligence as “oracle-like”—an intelligence that can function autonomously. In reality, AI will be most impactful and effectively adopted as it is used to augment human capabilities cooperatively. In 2023, we see the focus of AI shifting from a fully autonomous force to a powerful technology that facilitates cooperation between intelligent services and people—creating new, more valuable digital partnerships.
Calibrating AI to engender trust, relatability, and emotional connections with people can protect human autonomy and enable users to collaborate with intelligent systems as “digital partners.” New technology, including neural networks within generative AI, is inspiring an array of new cooperative AI skills—from artistic creation to code automation. It’s also sparking fundamental questions about the role of agency, creativity, and authenticity. It is important for product developers and businesses to leverage AI-enabled technologies in ways that engage human cooperation and not simply replace it. Only then will intelligent products offer valuable assistance and true digital partnerships that simplify people’s lives.
“I believe that anything that is manufactured, moves, or needs maintenance will be done with high levels of automation in the future. The way this will be done successfully is through a tight pairing of human and robot capabilities. So, instead of trying to replace a human worker with a robot, think about how automation can supercharge the human’s productivity and enjoyment of the work. This is a win-win for everyone.”
Roboticist Daniel Theobald – Vecna Robotics Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR)
What We See

Autonomous vehicles will be a reality in the distant future, but the difficulty of, and investment required, to replicate human intuition and sensitivity is highlighted by the fact that of the roughly 40 companies developing autonomous vehicles, most are shifting focus to assisted driving features in the near term while keeping their eye on the promise of truly autonomous vehicles in the future.
Audi chief technology officer Alexandre Haag has compared AID to GM’s self-driving unit, Cruise, and Ford’s unit, Argo. But Haag is pragmatic about the realities of getting autonomous fleets deployed, — of the technology. He said:
“Getting to 90 percent is fairly easy. Getting to 95 percent starts to get interesting. And then you still need to go way beyond that. Nine point nine nine nine nine… Adding each nine is ten times harder. When you’re at 95 percent, you’ve just scratched the surface.”
In 2023 companies will prioritize valuable assisted driving features that help drivers avoid accidents and provide comfort and safety. For example, Ford Motor company’s Active Drive Assist uses advanced computing of driver-facing camera data and radar sensing technology to enable real-time hands-free driving on certain sections of divided highways called Hands-Free Zones that make up over 100,000 miles of roads in the U.S. And, innovation isn’t limited to automakers. Apple CarPlay and Google Android Auto are continuing to enhance features that allow drivers to operate their phones through voice or one-touch. Android Auto is now in 150 million cars, with another 100 million expected to adopt the wireless version. Apple CarPlay comes standard in 80% of cars sold globally. In the U.S., 23% of buyers say it is a “must have”.
Increasingly realistic conversational AI experiences are engaging customers with natural language and accurate emotional sensitivities. Improvements in customer service applications are one area of focus, but other uses are surfacing as well. Microsoft’s $10B bet on OpenAI and ChatGPT seems to be well placed. For example, actor Ryan Reynolds used the tech to script a one minute commercial for Mint Mobile, which he owns. The resulting video received 195k views on YouTube within the first 24 hours. Terrifying…and exciting.
Advancements in natural language processing will enhance emotional AI experiences to connect with people more naturally. Sentiment analysis technologies will interpret emotions and seek more sensitive ways to relate with people. The degree of empathy and positive emotional responses will need to be balanced, so they don’t feel forced and unauthentic.
By setting rules and boundaries, ensuring transparency and accountability, and regularly reviewing and updating these guidelines, we can work toward establishing ethical guidance for AI. Developers should carefully and appropriately curate training data in order to prevent the assimilation of negative traits and tendencies such as racism and misogyny into our sentiment analysis and content synthesis technologies. For example, Microsoft’s experimental Twitter bot, Tay, served as a cautionary tale when it was released to the public on Twitter in 2016. It was taken down within 24 hours because it started to learn and regurgitate hateful, toxic content nearly immediately after launch.
Affective computing is the promise of creating effortless, integrated, and automatic ways of communicating emotions within our intimate social network. This could augment awareness systems and connectedness devices, reducing loneliness and improving health and well-being.

Generative AI and neural networks that create art, prose, and code are proliferating and raising questions of authenticity and agency. From stories, movies, paintings, images, video, and commercials, generative AI is helping people create. Data about human interactions with art are at the heart of training AI to generate artifacts that work. Yet, artistic inspiration, creation and consumption are truly human endeavors. As generative AI blurs the line between human and tech-driven creation, new relationships between artists and the tools they use to push boundaries will lead to new possibilities.
Generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Midjourney, RunwayML, etc. are producing outputs advanced enough to start to significantly impact the creative process and how it is perceived. The tools’ ability to produce thousands of options and iterations in unprecedented time will allow them to serve as a transformative catalyst to the exploratory stages of the creative process. However, these tools inherit a large number of creative and societal biases from their training data, and are often prone to ‘hallucinations’ — coming up with plausible-seeming but incorrect or nonsensical solutions. Taking on new roles as conductors as they adapt to capitalize on the strength of Humans + AI, human co-creators will play a critical role in establishing meaningful and responsible use cases for generative AI.
“Without sufficient guardrails, models like DALL·E 2 could be used to generate a wide range of deceptive and otherwise harmful content, and could affect how people perceive the authenticity of content more generally.
— OpenAI, creator of DALL-E 2
How to Prepare
- Research consumer and employee expectations to understand their expectations and experiences in cooperating with AI-enabled products, both explicit and implicit.
- Map cooperative AI workflows to assess where human empowerment and machine automation deliver the most value.
- Determine the persona and style of your intelligent systems with use of AI personas.
Immersive
Design for
Connection
Back to Reality
A vision of the Metaverse, fully immersive virtual worlds experienced via VR headsets, has been driven more by tech hype than by true consumer sentiment.
While virtual worlds will play some role in our future, mass adoption is further out. We see the Metaverse phenomenon as a mass desire to connect, participate in groups, and escape the day-to-day. The fantasy of a completely digital, ultimately customizable alternative world gained traction during the locked-down months of the pandemic, but as people return to more normal activities in the physical world, a more realistic view of immersive experiences is taking hold.
In 2023, we expect immersive experiences to be calibrated to meet people where they are, in reality, today. Products that naturally enrich connections across spaces, senses, and communities are gaining sustainable traction. We believe the Metaverse represents the next stage of spatial computing, enabling technology to integrate into living spaces, not just screens. In this way, spatial technology is becoming more aware of dynamic environments and allowing more immersive interactions across physical and virtual realities. Near-term solutions will eliminate technology barriers and create customer experiences that are fluid, intuitive, and enriching. This year, designers should calibrate multi-sensory interactions, spatial environments, and seamless ecosystems to create valuable immersive experiences that adapt to people and enable more natural interactions and connections.
What We See
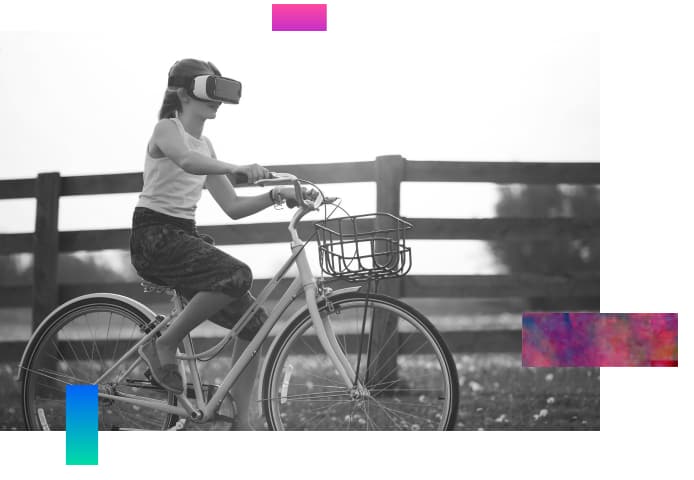

Spatial computing will deliver immersive experiences in the physical world via standard and augmented reality before mass adoption of virtualized metaverses due to the state of XR technology and consumer needs. While some analysts predict that 30% of all business will be ready to deliver some products in the Metaverse by 2026, the same report predicts that only 25% of consumers will spend one hour a day in the Metaverse.
The recent rise of immersive AR experiences across automotive, smart home, health, and enterprise technology industries is an example of companies focusing on solutions that meet customers’ nearer-term needs more effectively. The upcoming Apple mixed-reality headset demonstrates awareness that consumers want digital interactions that facilitate authentic connections and entertainment across spaces, senses, and communities.
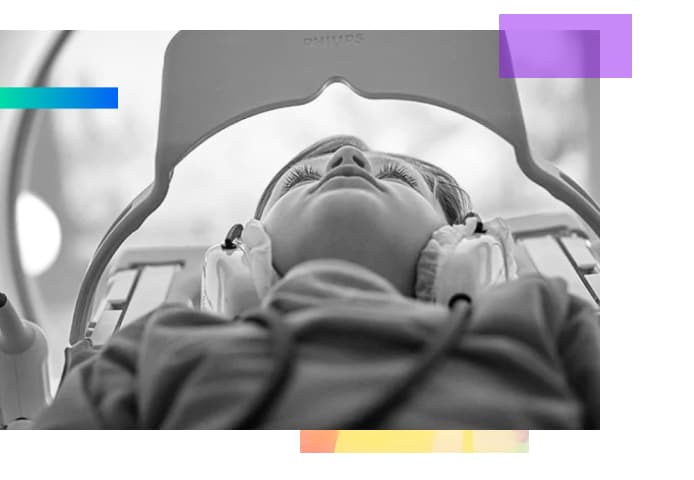

Immersive health is an example of leveraging immersive sensory modes to enhance patient experiences and reduce stress. For example, with the Philips Immersive MRI, patients personalize their experience by selecting a video theme. The video is projected onto the wall and viewed while inside the MRI machine via an easy-to-position mirror. Combined with sound, the experience becomes truly immersive.
In 2023, we see multi-sensory experiences continuing to weave rich narratives and storied experiences together for enriching entertainment, health, and work. Over-digitized and one-dimensional experiences will drive consumer defection. This will require all companies to explore how to deliver immersive experiences across the senses in both physical and digital worlds. Basic experiences will need an upgrade first over dream spaces.
“Using Philips Immersive MRI technology, hospitals found the number of patients requiring sedation during radiology scans dropped by 80%. In addition, they reported that 85% of parents said their children were less anxious while at the radiology department”
Philips Electronics Press Release, 2021

Immersive automotive experiences like voice and gesture control, haptic feedback, heads-up display, and assisted lane and collision control connect digital and physical spaces in more seamless, multimodal ways. These experiences improve safety and comfort. As these digital/physical capabilities evolve, the vehicle is becoming a “mini metaverse” of interaction and connectivity for today’s reality.
By 2028, in-car voice control will be embedded in nearly 90% of new vehicles sold globally. And, cockpit haptics technology is enabling tactile feedback in various areas of the car, improving safety through driver assistance and warning. Haptic feedback can decrease eyes-off-the-road time by 19% compared to visual warning systems alone. Haptics combined with innovations like heads-up display improve it further, to 39%. Research on near-future realities like gesture recognition, the use of sensors to read and interpret hand movements as commands, is taking hold. The automotive gesture control market is growing at over 17% per year and is being adopted by major car makers. Soon it will let users control infotainment, climate, and comfort settings without touching any buttons or screens.
How to Prepare
- Focus on reducing friction in existing experiences as a first step to more seamless, immersive experiences that are valuable to users.
- Avoid the hype and focus product strategies on alignment of immersive solutions that meet real human needs now, but that lead to greater innovation in the future.
- Expand 3D spatial design capabilities and skills to prepare for more multidimensional experiences in the future.
Systemic
Design for
Trust
Big Brain Trust
Web3 and blockchain promise a shift in power to the larger human community over corporate entities and a redefinition of ownership of personal data.
But, the promise needs to be better understood and trusted by the typical consumer. Instead, there is a rise in distrust exacerbated by high-profile failures in the industry. While the reality may lag, the bold and necessary promise of Web3 and blockchain is ultimate trust delivered by a trustless system—assuming computers are fail-safe, accurate, and maintained by scrupulous people.
We believe that in these early stages of Web3 and Blockchain, trust will need to be earned by institutions and individuals through complete transparency. As these decentralized systems evolve, businesses will benefit from connected people and groups, not simply connected products. Calibration of products that embody security, ultimate transparency, and control by users will make more rapid adoption of Web3 and Blockchain possible.
What We See

Consumers are embracing micro-communities like BeReal, VSCO, Discord, or Slack over large social media platforms as they seek more relevancy, authenticity, trusted community connections, and privacy. For example, Nextdoor, the popular platform that connects neighbors and facilitates discussion about local areas of interest, now has 33 million weekly active users across 280,000 neighborhoods.
While mega social platforms boast billions of active users, people recognize that these platforms are broadcast channels, designed for advertising rather than secure, trusted dialogue. People are increasingly aware that social media is easily manipulated, sometimes incorrect, and that users are subject to changing privacy policies. As a result, consumers are increasingly finding community and trusted connections in smaller, more intimate groups. For example, Audius aims to connect artists and fans assisted by decentralized technology. We think that product teams that convert users to collaborators by enabling connections between communities will build a base of more active, loyal customers.

Early adopters of technologies take on more systemic risks. Cryptocurrency, blockchain technology, and Web3, are riding the collective high-profiled hype cycle, yet have cost investors billions. When power is given to the individual, so is the responsibility to manage new forms of vulnerabilities. For example, the promise of Web3 has taken a hit as high-profile cases of fraud, crypto-crashes, and on-going volatility pervade the industry. The promise of trustless systems is meaningless when the people that build and operate the systems lack checks and balances. Beyond communicating user value propositions, innovators are responsible for protecting users through risk education. We see truly human-centric innovations being technology-agnostic as designers more carefully evaluate technology to find those that best serve users.
In the finance realm, efforts like stablecoins, which ties crypto value to the USD, hint at a necessary trend toward tethering the novel back to the familiar. Wharton Blockchain and Digital Asset Project, in collaboration with the World Economic Forum, wrote:
“Retail investors, professional traders, institutional actors, regulators, and policy-makers will need to temper enthusiasm for the innovative potential of DeFi with a clear understanding of its challenges.”
Brands are actively lowering the barrier of entry into Web3 experiences by using familiar terminologies and payment methods. New experiences such as Starbucks Odyssey – the coffee conglomerate’s NFT-based loyalty program, promises to ease complexity by not requiring a digital wallet or cryptocurrency to purchase NFTs. Instagram’s incorporation of NFT rebranded the term to “Digital Collectibles” for ease of comprehension and avoidance of technical jargon.

Web3 interoperability bridges services for more continuous experiences that empower users with flexibility and control. Tokenization is transforming ownership of data with more transparent systems. Examples such as the IBM Blockchain Platform and Patientory’s aggregation of user’s medical record data in a personal wallet, are giving us a view into a world where creators and consumers can expect more modularity and less redundancy when entering new services.
New ecosystems are being built with efficiency in mind. For example, Metamask is a browser plug-in that allows users to log-in to virtually any decentralized application (dApp), an application built on a decentralized network that combines a smart contract and a frontend user interface, with a single click. Instead of creating duplicate user profiles for each new dApp, users have all of their data stored on their wallet and simply connect it to the dApp.
Consumers are seeing more control with their own data in Web3. For example, Brave is an open-source web browser where user data is saved on a user’s device and not sent to Brave’s servers, ensuring that user data cannot be accessed by a third party. Users have the option to enable anonymously matched ads, which reward the user with a native cryptocurrency. Users have the ability to control ad frequency and the amount and type of data they share with advertisers.
How to Prepare
- Create digital spaces to foster conversations between content/product creators and fans.
- Invest in organizational transparency by acknowledging risks involved in participating in new systems and experiences.
- Balance equity and diversity across decentralized communal experiences with user councils and shared insights.
A More Conscious Future
In 2023, we see a critical theme of Conscious Calibration guiding innovation. Even though the winds may be shifting, digital transformation will continue. But, we believe it will be informed by a more sustainable approach that delivers longer-term value. In this complex environment, successful innovation will meet increasingly nuanced user needs across digital and physical activities. To that end, designers must consciously calibrate innovation to align with users’ expectations across the four dimensions of digital transformation – creating more intelligent, immersive, systemic, and social experiences.

Download FutureView 2023 trend report to learn more about how to drive successful product innovation.






